Weight training workout women is more than just lifting weights; it’s a transformative journey toward enhanced physical and mental well-being. This guide delves into the numerous benefits women experience from weight training, from increased bone density and metabolism boosts to improved self-esteem and stress reduction. We’ll explore tailored workout programs for various fitness levels, detailing effective exercises with proper form and technique, and address common concerns women may have about starting a weight training regimen. Finally, we’ll emphasize the importance of proper nutrition to support muscle growth and recovery.
Understanding the nuances of weight training specifically designed for women is key to achieving optimal results and avoiding potential pitfalls. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced lifter, this guide provides valuable insights and practical strategies to help you reach your fitness goals safely and effectively.
Benefits of Weight Training for Women
Weight training offers a multitude of advantages for women, extending far beyond simply building muscle mass. It’s a powerful tool for improving overall health, well-being, and quality of life, impacting both physical and mental aspects. This section details the significant benefits women can experience through consistent weight training.
Physiological Benefits of Weight Training for Women
Weight training provides substantial physiological benefits. Increased bone density is a key advantage, especially crucial for women as they age and risk of osteoporosis increases. The stress placed on bones during weightlifting stimulates bone growth and strengthens existing bone tissue, mitigating age-related bone loss. Furthermore, weight training significantly boosts metabolism. Increased muscle mass resulting from weight training burns more calories at rest, leading to more efficient weight management and improved body composition. Finally, weight training enhances muscle tone and strength, resulting in a more defined physique and improved physical functionality in daily activities. These improvements contribute to a more active and independent lifestyle as women age.
Psychological Benefits of Weight Training for Women
Beyond the physical, weight training offers significant psychological benefits. The feeling of accomplishment from achieving progressively heavier lifts or mastering new exercises significantly boosts self-esteem and confidence. Weight training can also serve as a powerful stress reliever. The physical exertion involved releases endorphins, natural mood boosters that alleviate stress and anxiety. The structured routine and focus required during workouts can provide a sense of control and accomplishment, further contributing to improved mental well-being. The social aspect of group fitness classes, if chosen, can also increase feelings of belonging and support.
Comparison of Weight Training to Other Forms of Exercise for Women
While cardiovascular exercise like running or swimming is essential for heart health, weight training uniquely addresses bone density and muscle mass. Yoga and Pilates improve flexibility and core strength, but they don’t offer the same muscle-building and metabolic benefits as weight training. Weight training complements other forms of exercise, creating a well-rounded fitness program that addresses multiple aspects of health. For example, a combination of cardio, weight training, and flexibility exercises offers the most comprehensive approach to overall fitness and well-being for women.
Summary of Key Benefits of Weight Training for Women
| Physical Well-being | Mental Well-being | Physical Well-being | Mental Well-being |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Bone Density | Increased Self-Esteem | Improved Metabolism | Stress Reduction |
| Enhanced Muscle Tone and Strength | Improved Body Image | Improved Body Composition | Increased Confidence |
| Increased Physical Function | Sense of Accomplishment | Reduced Risk of Osteoporosis | Improved Mood |
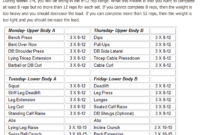
Common Exercises for Women
Choosing the right exercises is crucial for building strength, improving fitness, and achieving your personal goals. This section details effective compound and isolation exercises suitable for women of all fitness levels, emphasizing proper form to maximize results and minimize injury risk. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or certified trainer before starting any new workout routine.
Compound Exercises for Women
Compound exercises work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making them highly efficient for building overall strength and burning calories. These exercises are foundational for a well-rounded fitness program.
- Squats: Imagine a picture: a woman standing with feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly outward. She lowers her hips as if sitting in a chair, keeping her back straight and chest up. Her knees track over her toes. This exercise primarily targets the quadriceps, glutes, and hamstrings. Maintaining a straight back prevents lower back injury. Variations include goblet squats (holding a weight at chest height) and barbell back squats (weight across the upper back).
- Deadlifts: Picture a woman standing with feet hip-width apart, a barbell in front of her. She bends at her hips and knees, keeping her back straight, and grasps the bar with an overhand grip, slightly wider than shoulder-width. She then lifts the bar, extending her hips and knees simultaneously, maintaining a neutral spine. This targets the posterior chain (glutes, hamstrings, and lower back). Proper form is essential to prevent back injury; focusing on hinging at the hips rather than bending at the waist is key.
- Bench Press: Visualize a woman lying on a bench with feet flat on the floor, holding a barbell above her chest with a slightly wider than shoulder-width grip. She lowers the bar to her chest, keeping her elbows slightly bent, then pushes it back up. This works the chest, shoulders, and triceps. Ensuring a stable base and controlled movement is crucial to prevent shoulder injuries.
- Overhead Press: Imagine a woman standing with feet shoulder-width apart, holding a barbell or dumbbells at shoulder height. She presses the weight overhead, extending her arms fully, keeping her core engaged and back straight. This targets the shoulders and triceps. Maintaining a controlled movement and avoiding locking out the elbows minimizes the risk of shoulder injury.
- Bent-Over Rows: Picture a woman bending at her hips, keeping her back straight, with a barbell or dumbbells in her hands. She pulls the weight towards her chest, squeezing her shoulder blades together. This exercise targets the back muscles (lats, rhomboids, trapezius). Maintaining a flat back is crucial to avoid back strain.
- Lunges: Visualize a woman stepping forward with one leg, bending both knees to 90 degrees. Her front knee should be aligned with her ankle, and her back knee should hover just above the ground. This exercise works the quads, glutes, and hamstrings. Maintaining balance and proper knee alignment prevents knee injuries.
Isolation Exercises for Women
Isolation exercises target a single muscle group, allowing for more focused muscle development and improvement in muscle definition. These are often used to supplement compound exercises.
- Bicep Curls: Imagine a woman standing with dumbbells in each hand, palms facing forward. She curls the weights towards her shoulders, keeping her elbows close to her sides. This targets the biceps. Controlled movements prevent strain on the elbows and wrists.
- Triceps Extensions: Picture a woman holding a dumbbell overhead with both hands, then lowering the weight behind her head by extending her elbows. This isolates the triceps. Maintaining a controlled movement prevents elbow injury.
- Lateral Raises: Visualize a woman standing with dumbbells in each hand, arms at her sides. She raises her arms out to the sides until they are parallel to the floor, keeping a slight bend in her elbows. This targets the lateral deltoids (side of the shoulders).
- Hamstring Curls: Imagine a woman lying face down on a hamstring curl machine, hooking her ankles under the padded bar. She then curls the weight towards her glutes, contracting her hamstrings. This exercise specifically targets the hamstrings.
- Calf Raises: Picture a woman standing with her feet shoulder-width apart, either on a flat surface or a slightly raised platform. She raises up onto her toes, engaging her calf muscles, then lowers back down. This exercise isolates the calf muscles.
Comparison of Compound and Isolation Exercises
Compound exercises are more efficient for building overall strength and burning calories due to their multi-muscle engagement. Isolation exercises are valuable for targeting specific muscle groups to improve muscle definition and address muscle imbalances. A well-rounded program incorporates both types of exercises for optimal results. For example, a woman aiming for overall fitness would benefit from squats and deadlifts (compound) complemented by bicep curls and triceps extensions (isolation) to achieve a balanced and well-defined physique.
Last Point
Embarking on a weight training journey as a woman offers a wealth of physical and mental rewards. By understanding the benefits, designing a suitable program, mastering proper form, and prioritizing nutrition, you can unlock your full potential. Remember, consistency and a focus on proper technique are crucial. Don’t hesitate to consult with fitness professionals for personalized guidance and support. Embrace the power of weight training and experience the transformative changes it can bring to your life.